Generative AI is powerful, but moving it from a public demo to a secure, enterprise-grade application is a major challenge. The biggest hurdle is connecting LLMs to your company’s private data while maintaining strict governance and reliability. This is precisely the problem the Databricks Data Intelligence Platform is designed to solve.
By unifying data, analytics, and AI on a single Lakehouse architecture, Databricks provides the foundation to build, train, and deploy custom GenAI. This guide provides a practical, step-by-step walkthrough on how to use Databricks for generative AI. We’ll cover the essentials, from preparing your data and building RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) applications to deploying and monitoring your models in production.
What is Databricks and Why It Powers Generative AI
At its core, Databricks is built on the Lakehouse architecture, which unifies data, analytics, and AI on a single platform. Unlike traditional systems that create silos between data warehouses (for BI) and data lakes (for AI), the Lakehouse allows you to manage one copy of your data for all workloads.
For generative AI, this unified approach is a game-changer. It provides:
- Scalable Data & Compute: Easily manage massive datasets required for training and fine-tuning models using scalable compute.
- Unified Governance: Apply a single governance model to all your data and AI assets, which is critical for managing sensitive information used by LLMs.
- Integrated Tooling: Databricks integrates seamlessly with its own tools, like Mosaic AI, and third-party models, enabling a complete generative AI and LLM solution.
This ecosystem is designed to support the latest AI advancements. It provides native capabilities for fine-tuning open-source models and building sophisticated RAG applications, allowing you to augment LLMs with your private enterprise data for accurate, context-aware responses.
Key Features for Generative AI Development
To successfully build generative AI applications, you need a robust set of tools for the entire lifecycle. Databricks provides this through three core components:
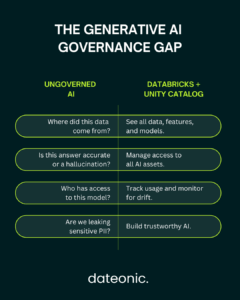
- Unity Catalog: This is the foundation for fine-grained governance in the Lakehouse. For generative AI, it allows you to manage access, audit, and track the lineage of all assets, including models, features, and the data used to train them. This ensures your AI applications are secure and compliant.
- MLflow: An open-source platform for managing the end-to-end machine learning lifecycle. In a GenAI context, MLflow is crucial for MLOps, allowing you to track experiments, log prompts and model outputs, package models for deployment, and monitor their performance in production.
- Delta Lake: The open-source storage layer that brings ACID transactions and reliability to your data lake. For AI, this means your models are fed by high-quality, reliable data pipelines, which is essential for accurate, trustworthy results.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use Databricks for Generative AI
This section provides a practical walkthrough for building a generative AI application on the Databricks platform.
Step 1: Set Up Your Databricks Workspace
Before you can build, you must lay the foundation. This starts with configuring your Databricks workspace.
- Create Your Workspace: Sign up for a Databricks account on your cloud provider of choice (AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud).
- Configure Compute: Set up Databricks clusters with GPU acceleration. This is critical for the computationally intensive tasks of model training, fine-tuning, and inference.
- Ingest Data: Use tools like Delta Live Tables to build reliable, streaming data pipelines. Following a Medallion Architecture, you can land raw data in a 'Bronze’ table, clean and validate it into 'Silver’, and aggregate it into 'Gold’ tables ready for AI.
Step 2: Explore and Prepare Data for Gen AI
The quality of your generative AI application is entirely dependent on the quality of your data.
- Use Databricks Notebooks for interactive data exploration and cleaning.
- Prepare your data for AI. For RAG, this involves „vectorization” – converting your text data into numerical representations called embeddings using models from providers like Hugging Face.
- Store these embeddings in a Delta Lake table, which will serve as your knowledge base.
You can easily integrate data from diverse sources, whether it’s unstructured text from AWS S3, structured data from relational databases, or real-time data from streaming platforms.
Step 3: Build and Fine-Tune Models
This is where you bring your generative AI application to life. Databricks supports multiple patterns:
- Implement RAG: This is the most common pattern for building chatbots and Q&A systems.
- Use Databricks Vector Search to efficiently index your embeddings (from Step 2) and find the most relevant documents for a user’s query.
- Pass this relevant context, along with the user’s query, to an LLM (like Llama 3 or GPT-4) via the Mosaic AI Foundation Model APIs.
- The LLM then generates an answer based only on the context you provided, reducing hallucinations and ensuring responses are grounded in your company’s data.
- Fine-Tune Models: For more specialized tasks, you can use Mosaic AI to fine-tune an open-source model on your own domain-specific data. This adjusts the model’s weights to make it an expert in your specific terminology and business logic.
Step 4: Deploy and Monitor Gen AI Apps
A model in a notebook provides no business value. You must deploy it as a scalable application.
- Package the App: Use the Databricks Apps framework to package your RAG pipeline – which includes the vector search, prompting logic, and LLM call – into a single, deployable application.
- Deploy as an Endpoint: Use Databricks Model Serving to deploy your app as a scalable REST API endpoint. This allows other applications to easily call your GenAI service.
- Govern and Monitor: This is where Unity Catalog shines. You can track all requests to your endpoint, monitor for cost and performance, and ensure that only authorized users and services can access the application, providing end-to-end AI governance.
Step 5: Scale with MLOps
To scale your generative AI initiatives, you must automate the entire process using MLOps.
- Use MLflow to log all components of your RAG application, including the specific model versions and prompts used.
- Automate your data-prep and fine-tuning pipelines using Databricks Workflows or CI/CD tools.
- This creates a reproducible system where you can easily update your knowledge base, retrain your model, and deploy new versions with minimal manual effort. This approach is fundamental to a modern AI strategy.
Real-World Use Cases: Databricks in Action
Databricks is already powering generative AI applications across industries. As noted in recent updates, the partnership between SAP and Databricks highlights the trend of using AI agents for:
- Finance: AI agents that process claims faster and improve cash flow.
- Sales & Service: Agents that accelerate business processes and streamline customer inquiries for faster resolution.
- Marketing: Automating the creation of targeted content and campaign descriptions.
The table below compares a traditional, siloed approach to AI with the unified Databricks workflow.
| Use Case | Traditional Challenge | Databricks Solution | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content Generation | Data silos; slow manual processes | Unified Lakehouse + LLMs | 5x faster content creation |
| Predictive Analytics | Model drift; poor data quality | MLflow Monitoring + Delta Lake | 90% accuracy boost |
| Customer Support Bot | Stale, generic answers | RAG with Databricks Vector Search | Real-time, accurate answers |
Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
As you build, keep these best practices in mind:
- Prioritize Data Quality: Your generative AI app is only as good as your data. Use Delta Live Tables to enforce quality constraints.
- Secure Your Keys: Store API keys for external models (like OpenAI) securely using Databricks Secrets.
- Optimize Costs: Use auto-scaling clusters and monitor endpoint usage to control compute costs.
The most common pitfall is overlooking governance. Without a tool like Unity Catalog, it’s easy to lose track of data lineage and model permissions, leading to compliance issues and untrustworthy AI.
Conclusion
Databricks democratizes how to use Databricks for generative AI by providing a single, scalable platform for the entire lifecycle. It moves generative AI from a siloed experiment to a fully governed, production-scale enterprise capability, enabling you to innovate safely and at scale.
Ready to implement generative AI on the Lakehouse? Partner with Dateonic, the official Databricks consulting experts, for tailored AI-ready platforms.
Visit Dateonic to browse our resources or schedule a free consultation to unlock your generative AI potential today.
