Is your Hadoop system becoming a bottleneck? If you’re struggling with high maintenance costs, scalability issues, and a complex ecosystem, it’s time for a change.
In this guide, I provide a straightforward path to migrate from Hadoop to Databricks, helping you move from a legacy setup to a modern, unified data platform. We’ll cover the essential steps, benefits, and common pitfalls to ensure your transition to the Databricks Lakehouse is smooth and successful, unlocking better performance, governance, and AI capabilities for your business.
Why Migrate from Hadoop to Databricks?
The move from Hadoop to Databricks is driven by a clear set of advantages that address the limitations of legacy systems. The business case for migration is compelling, with real-world motivations centered on reducing operational costs and enabling real-time analytics.
- Cost-Effective Scaling: Databricks’ cloud-native architecture allows for the separation of storage and compute, enabling organizations to scale resources independently and pay only for what they use. This is a significant departure from Hadoop’s rigid and often underutilized infrastructure.
- Simplified Management: Databricks provides a fully managed platform that automates many of the complex tasks associated with Hadoop, such as cluster management, performance tuning, and security. This frees up data teams to focus on higher-value activities. For a deeper dive into cluster optimization, see our guide on optimizing clusters in Databricks.
- Accelerated Innovation with AI/ML: Databricks is built on Apache Spark and offers an integrated environment for data science and machine learning. This accelerates the development and deployment of AI/ML models, enabling organizations to innovate faster.
- Unified Governance: The Databricks Unity Catalog provides a centralized governance solution for all data and AI assets, ensuring data quality, security, and compliance across the organization.
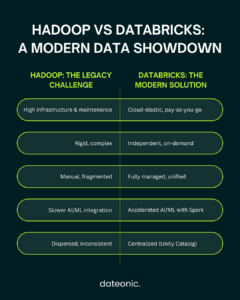
The challenges with Hadoop are not just technical but also impact the bottom line. Reliability issues, significant infrastructure overhead, and the limitations of cloud-managed services like EMR or HDInsight all contribute to a higher total cost of ownership.
Preparing for Your Migration
A successful migration requires careful planning and preparation. A well-defined strategy will minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition to the Databricks Lakehouse Platform.
- Assess your Hadoop environment: The first step is to create a detailed inventory of your existing Hadoop ecosystem. This includes:
- Data storage (HDFS, Hive, HBase)
- Data pipelines (Spark, MapReduce, ETL tools)
- Metadata (Hive Metastore)
- Workloads and their dependencies
- Choose your migration approach: There are several approaches to migrating from Hadoop to Databricks. The right choice will depend on your specific requirements and timeline.
- Lift-and-shift: This approach involves moving your existing workloads to Databricks with minimal changes. It’s the fastest option but may not fully leverage the capabilities of the platform.
- Replatforming: This involves making some modifications to your workloads to take advantage of Databricks’ features, such as Delta Lake and Unity Catalog.
- Refactoring: This approach involves redesigning your applications to be cloud-native and fully optimized for the Databricks platform. It offers the greatest long-term benefits but requires more effort.
- Develop a planning roadmap: A detailed roadmap should be created with clear goals, timelines, and responsibilities. It should also include a risk management strategy to address potential challenges.
| Strategy | Effort & Time | Cost | Databricks Optimization | Best For… |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lift-and-Shift | Low | Low | Minimal | Quick, non-critical workloads; initial PoCs. |
| Replatform | Medium | Medium | Good | Core workloads needing improved reliability & performance. |
| Refactor | High | High | Maximum | Mission-critical applications where full cloud-native benefits are desired. |
Step-by-Step Guide to Migrate from Hadoop to Databricks
The migration process can be broken down into five key steps. Following a structured approach will ensure a successful and efficient transition.
- Data Migration: The first step is to move your data from HDFS to a cloud storage service like Amazon S3, Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS), or Google Cloud Storage. Tools like DistCP can be used for this purpose. Once in the cloud, it’s recommended to convert your data to the Delta Lake format to take advantage of its reliability and performance features.
- Metadata and Governance Migration: The Hive Metastore can be migrated to the Databricks Unity Catalog. This will provide a centralized and unified governance model for all your data and AI assets. Security policies and access controls should be standardized to ensure compliance.
- Workload Adaptation: This is a critical step that involves migrating your existing workloads to the Databricks platform.
- Spark jobs: Existing Spark jobs can be migrated with some modifications to update Spark versions and replace RDDs with DataFrames where possible.
- Non-Spark workloads: Other workloads, such as Hive queries or ETL jobs, will need to be converted to run on Databricks.
- Testing and Optimization: Once your workloads have been migrated, it’s essential to validate data integrity and benchmark performance. Automated diffing and checksums can be used to ensure data accuracy. Clusters should be optimized for performance and cost-efficiency.
- Go-Live and Decommissioning: After successful testing, you can go live with your new Databricks environment. User training and support are crucial during this phase. Once the new platform is stable, the legacy Hadoop systems can be decommissioned.
For organizations looking to accelerate their migration, partnering with a Databricks expert like Dateonic can provide the necessary expertise and support. Learn more about our Databricks implementation services.
Common Pitfalls When Migrating from Hadoop to Databricks and How to Avoid Them
Migrating from Hadoop to Databricks is a complex undertaking, and there are several common pitfalls that can derail the process. Being aware of these challenges and having a plan to address them is key to a successful migration.
- Inadequate Planning: A lack of detailed planning can lead to disruptions and unexpected costs. To avoid this, create a comprehensive inventory of your existing environment and develop a phased rollout plan.
- SQL Dialect and Architecture Mismatches: Hadoop and Databricks have different SQL dialects and architectures. This can lead to compatibility issues and require significant code changes. Using automated translation tools and having a coexistence period with external metastores can mitigate this risk.
- Data Validation Issues: Ensuring data integrity during and after the migration is critical. Use automated diffing and checksums to validate your data at every stage of the process.
- Skills Gaps: Your team may not have the necessary skills to manage a Databricks environment. Address this by providing training or partnering with an experienced Databricks consultant.
At Dateonic, we have extensive experience in data platform modernization and have helped numerous organizations successfully migrate to Databricks. Our expertise, as highlighted in our work on Lakehouse Federation, allows us to anticipate and avoid these common pitfalls, ensuring a smooth and successful migration.
Conclusion
Migrating from Hadoop to Databricks is a strategic imperative for organizations looking to modernize their data platform and unlock the full potential of their data. By following a structured approach and being aware of the common pitfalls, you can ensure a successful transition.
Ready to start your migration journey? Contact Dateonic for expert guidance on your migration from Hadoop to Databricks. Start modernizing your data platform today.
