Databricks, through Delta Tables, provides a powerful tool for large-scale data management, delivering reliability, performance, and governance.
As a Databricks expert, I present a comprehensive technical guide that explains what Delta Tables are, why they are essential in modern data architectures, and how to leverage them for robust data pipelines.
What Is a Delta Table?
A Delta Table is a storage layer in Databricks that enhances traditional data lakes by adding a transactional layer, ensuring data reliability and consistency.
Built on the open-source Delta Lake, Delta Tables support ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) transactions, enabling concurrent read and write operations without data corruption.
Data is stored in Parquet format, enriched with a transaction log that records all changes, supporting features like time travel and schema evolution.
Why Delta Matters in Modern Data Architectures
Delta Tables address key limitations of traditional data lakes, transforming them into robust lakehouse architectures. Their significance stems from the following:
- Solves the “Data Swamp” Problem: Traditional data lakes often become disorganized due to inconsistent data and lack of governance. Delta Tables enforce schema validation and provide metadata management, ensuring data quality.
- Makes Lakes Queryable, Reliable, and Auditable: With ACID transactions, Delta Tables ensure data consistency, support SQL queries, and enable auditing through versioning.
- Enables Unified Support for Streaming and Batch Data: Delta Tables seamlessly integrate batch and streaming workloads, enabling real-time analytics on unified datasets.
- Core Component of Lakehouse Architecture: By bridging data lakes and warehouses, Delta Tables provide a single platform for analytics, machine learning, and data governance.
Key Features
Delta Tables offer a comprehensive set of features that streamline data management:
- ACID Transactions: Ensure data consistency in concurrent environments, preventing partial writes or data corruption.
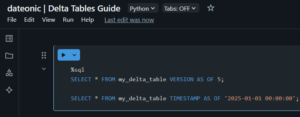
- Time Travel (Data Versioning): Query historical data snapshots to audit changes or recover from errors. For instance:
SELECT * FROM my_delta_table VERSION AS OF 5;
or
SELECT * FROM my_delta_table TIMESTAMP AS OF '2025-01-01 00:00:00′;
- Upserts, Deletes, Merges (Change Data Capture): Support efficient data modifications via MERGE INTO, enabling Change Data Feed (CDF) for incremental updates.
- Schema Enforcement and Evolution: Enforce schema validation and support schema evolution. By enabling auto-merge, you can append data with new columns:
spark.conf.set(„spark.databricks.delta.schema.autoMerge.enabled”, „true”)
- Fast Performance via Indexing and Caching: Utilize indexing, caching, and Z-order indexing for faster query execution, as detailed in Databricks Performance Techniques.
- Supports Unity Catalog for Data Governance: Integrate with Unity Catalog for centralized access control and compliance.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| ACID Transactions | Ensures data consistency across concurrent operations. | Prevents data corruption in multi-user environments. |
| Time Travel | Queries historical data snapshots using version or timestamp. | Facilitates auditing and error recovery. |
| Upserts and Merges | Supports MERGE INTO for efficient data modifications. | Simplifies ETL with Change Data Feed. |
| Schema Enforcement | Validates data against defined schemas, with auto-merge for evolution. | Maintains data quality and adapts to changes. |
| Performance Optimization | Uses indexing and caching for faster queries. | Enhances query speed, as per Performance Techniques. |
| Unity Catalog Integration | Centralizes access control and compliance. | Ensures governance, detailed in Unity Catalog. |
How to Create a Delta Table
Creating a Delta Table in Databricks is straightforward using Python or SQL.
Python Example:
# Assuming df is a DataFrame
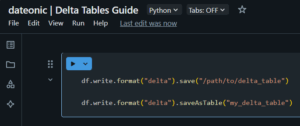
df.write.format(„delta”).save(„/path/to/delta_table”)
Or, to create a managed table:
df.write.format(„delta”).saveAsTable(„my_delta_table”)
SQL Example:
CREATE TABLE my_delta_table
USING DELTA
AS SELECT * FROM source_table
To convert an existing Parquet table to Delta:
CONVERT TO DELTA my_parquet_table

For more on setting up a Databricks environment, refer to Getting Started with Databricks.
Use Cases
Delta Tables are versatile and support various scenarios:
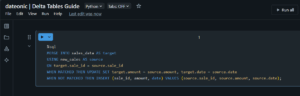
- Reliable ETL Pipelines: Delta Tables support MERGE INTO operations, allowing efficient management of inserts, updates, and deletes. For example, to update sales_data with new_sales:
MERGE INTO sales_data AS target
USING new_sales AS source
ON target.sale_id = source.sale_id
WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET target.amount = source.amount, target.date = source.date
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT (sale_id, amount, date) VALUES (source.sale_id, source.amount, source.date);
- Machine Learning Feature Stores: Versioning tracks feature changes, ensuring reproducibility in ML experiments.
- Real-Time Analytics: Combine batch and streaming data for up-to-date insights.
- Data Auditing and Compliance: Time travel enables queries on historical data states, meeting audit requirements.
Best Practices
To help you get the most out of Delta Tables, I’ve prepared a quick infographic highlighting the key best practices:

What’s Next?
- To get hands-on experience with Delta Tables, sign up for the Databricks Community Edition, where you can experiment with the features discussed in this article for free. Select „Personal use” to access the Community Edition.
- Explore more Databricks features through related articles:
- For further information or tailored implementations, contact us.